Research Scientist
Cardiac Surgery
the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center
Determining the cytoplasmic and membranous localization of CD38 using ImageStream
Yong Gyu Lee1,2, Jung-Lye Kim1,2, Joanna M Marshall1,2, Doug A Gouchoe1,2, Bryan A Whitson1,2, Sylvester M Black1,2.
1COPPER Laboratory, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, OH, United States; 2Surgery, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, OH, United States
Background: CD38 is a membrane-associated ecto/endoenzyme that is abundantly expressed on numerous human cells, particularly those of hematopoietic origin. Within the liver, CD38 is found on both Kupffer Cells and infiltrating macrophages, as well as hepatic stellate cells (constitutively expressed – increased with cell activation). CD38 is a multifunctional ectoenzyme that catalyzes the synthesis and hydrolysis of cyclic ADP-ribose (cADPR) from NAD+ to ADP-ribose. These reaction products are essential for the regulation of intracellular Ca2+. The CD38 protein is also marker of cell activation. Activated hepatocytes are present in all livers but are increased in injured and marginal organs, which thus express CD38 in greater amounts. When transplanted, marginal organs are known to be much more susceptible to ischemic-reperfusion injury (IRI), as compared to standard criteria donor organs. In this study, we demonstrate the use of imaging flow cytometry, ImageStream, and show the potential for this technology to address the unmet need to monitor cellular expression and localization of CD38.
Methods: ImageStream technology is a novel technology that combines flow cytometry and microscopy. In this work primary hepatocytes were isolated and labeled using a panel of cellular markers. This antibody cocktail was complimented with a differential intracellular/extracellular labeling strategy to identify CD38 intensity and localization on each cell population. Traditional gating of populations was augmented by a novel software-based masking strategy to simultaneously quantitate and differentiate subcellular localization of CD38. We employed this strategy to monitor CD38 protein expression, with high resolution and throughput, in a fatty liver injury model.
Results: Each of the four major liver cell types- hepatocytes (HCs), hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), Kupffer cells (KCs), and liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs)- express CD38 to varying degrees at baseline. HCs show the lowest levels of CD38 expression with a predominance of intracellular expression, while LSECs, KCs, and HSCs show high surface expression of CD38. Moreover, we quantified CD38 cellular distribution ratio by calculating proportion of total CD38 contributed by surface vs cytoplasm vs. nucleus. The surface: cytoplasm: nucleus ratio for CD38 localization in primary rat liver cells at baseline are as follows: 16% : 67% : 17% for hepatocytes, 80% : 6% : 14% for HSCs, 90% : 6% : 4% for LSECs, and 69% : 28% :3% for KCs.
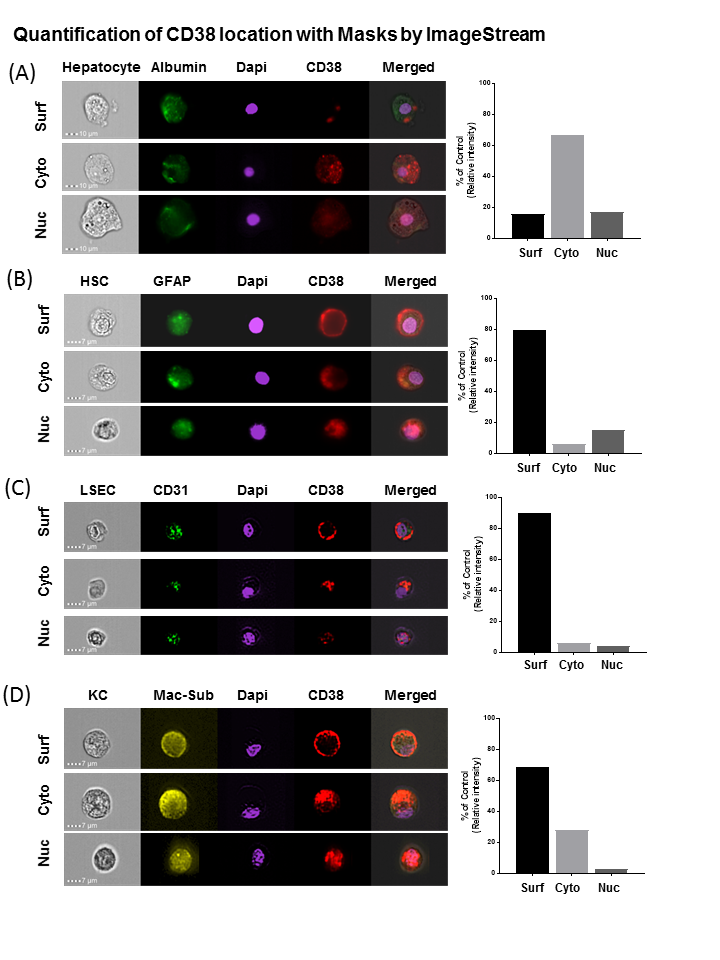
Conclusions: We have optimized an ImageStream technique that will allow us to efficiently and effectively determine shifts in CD38 location and to more accurately quantify expression of the biomarker CD38. This strategy may allow us to capture more information we can use for targeting therapeutics, or for use in prediction of function for marginal organs. Future studies will use this strategy to predict marginal organ function post-transplantation with human liver biopsies. This technique can be expanded to other molecules or biomarkers with multiple subcellular locations or transitions.
This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (R01ADK123475 to SMB and R01AHL143000 to BAW).
References:
[1] Laurence Britton. Hepatic iron concentration correlates with insulin sensitivity in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol Commun. 2018 Apr 27;2(6):644-653.
[2] Moumita Paul-Heng. Direct recognition of hepatocyte-expressed MHC class I alloantigens is required for tolerance induction. JCI insight. 2018;3(15):e97500.
[3] Thaddeus C George. Distinguishing modes of cell death using the ImageStream multispectral imaging flow cytometer. Cytometry A. 2004 Jun;59(2):237-45.
[4] Junjie Zhu. Cell Type-Specific Roles of CD38 in the Interactions of Isoniazid with NAD+ in the Liver. Drug Metab Dispos
. 2020 Dec;48(12):1372-1379.
[5] Laura F.Ogle. Imagestream detection and characterisation of circulating tumour cells – A liquid biopsy for hepatocellular carcinoma? J Hepatol. 2016 Aug;65(2):305-13.
Lectures by Yonggyu Lee
| When | Session | Talk Title | Room |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Sun-30 16:40 - 18:00 |
Abstracts Session 1 | Determining the cytoplasmic and membranous localization of CD38 using ImageStream | Grand Georgian |
